Page 14 - Copper-associated hepatitis in the Labrador retriever diagnosis, treatment and genetics
P. 14
Chapter 1
life25 (Table 1). The disease incidence is estimated to be 1 in 30,00026. A wide variety of mutations in ATP7B have been described (http://www.wilsondisease. med.ualberta.ca) and most patients are compound heterozygotes27. There is a lack of correlation between the genotype and the phenotype and individuals carrying the same mutation can show distinct clinical signs, which poses major difficulties for diagnosing the disease28;29. Other genes or environmental influences are thought to modify clinical expression of the disease, but have not yet been identified30.
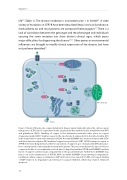
Figure 1 Model of hepatocyte copper metabolism. Copper (green diamond) enters the cell via copper transporter 1 (CTR1) and is sequestered in the cytoplasm by the small molecules metallothionein (MT) and glutathione (GSH). Shuttling of copper to the destination molecules takes place via copper chaperones (pink). COX17 shuttles copper to the cytochrome C oxidase (CcO) in the mitochondria. CCS is the chaperone for superoxide dismutase (SOD1). Recently COMMD1 was shown to interact with SOD1 and this interaction requires CCS-mediated copper incorporation in SOD1. ATOX1 transports copper to ATP7B in the trans Golgi network, where incorporation of copper in apo-ceruloplasmin (CP) takes place. Holo-ceruloplasmin is subsequently excreted in the plasma. The precise mechanism for export of excess copper in the bile is not completely resolved, but it is hypothesized that ATP7B and COMMD1 mediate fusion of copper-loaded vesicular compartments to the apical membrane. Furthermore, COMMD1 may play a role in the maintenance of ATP7B. XIAP can inhibit COMMD1 by promoting its degradation, resulting in cellular copper accumulation. XIAP itself can receive copper from CCS, and copper binding of XIAP results in its degradation and decrease in caspase inhibition, which may result in enhanced apoptosis.
CTR1
MT
GSH GSH
GSH
COX17
CcO
Mitochondrion
COMMD1
MT
MT
CCS
CCS
SOD1
P XIAP
ATP7B
XIA
AP
ATOX1
ATP7B
CP
Bile canaliculus
AM
CO
7BD1
TPM
Golgi apparatus Plasma
Lysosome
C
C
P
P
12